Growth and Yield of Inpari 29 Rice Varieties on Raised-bed and Different Depths of Sunken-bed in Saline Field
Nasrudin Nasrudin(1*), Budiastuti Kurniasih(2)
(1) Faculty of Agriculture Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta
(2) Faculty of Agriculture Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
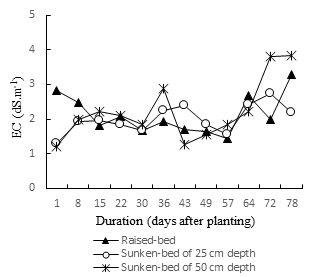
Increased productivity of rice is required to meet the increasing food demand. Utilization of marginal lands, such as saline land is one of the solutions applicable to increase rice production. The objective of this study was to determine the growth and yield of Inpari 29 rice variety planted on raised-bed and different depths of sunken-bed in saline field. This study used the Split Plot Design with two treatments. The depth as the main plot consisted of two depth levels: a depth of 50 cm and a depth of 25; and the planting area field as the subplot that consisted of two levels: raised-bed and sunken-bed. The treatment was repeated three times. The rice planted in sunken-bed showed higher growth than in raised-bed as indicated by the high content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll, nitrate reductase activity and plant height. The rice planted in the sunken-bed yielded higher than in raised-bed as indicated by higher harvest index and the weight of grain per clump. Rice planted in 25 cm depth showed higher nitrate reductase activity and grain weight per clump than in 50 cm depth.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Ai, N.S. and Y. Banyo. 2011. Konsentrasi klorofil daun sebagai indikator kekurangan air pada tanaman. Jurnal ilmiah sains., 11: 166-173.
Aref, F. 2013. Effect of Saline Irrigation Water on Yield and Yield Components of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). African Journal of Biotechnology., 12: 3503-3513.
Balai Penelitian Tanah. 2009. Analisis kimia tanah, tanaman, air, dan pupuk. Bogor: Balai Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pertanian, Departemen Pertanian.
BB Padi. 2012. Deskripsi padi Varietas Inpari 29. http://bbpadi.litbang.pertanian.go.id/index.php/varietas/inbrida-padi-sawah-irigasi-inpari/content/item/32-inpari-29-rendaman
Bruins, R.J.F., C. Shuming., C. Shijian and W.J. Mitsch. 2012. Ecological engineering strategies to reduce flooding damage to wetland crops in central China. Ecological Engineering., 11:231-259.
Cha-um, S. and C. Kirdmanee. 2010. Effect of Glycinebetaine on Proline, Water Use, and Photosynthetic Efficiencies, and Growth of Rice Seedlings Under Salt Stress. Turk Journal Agricultural Forestry., 34:517-527.
Ella, E. S., N. Kawano and O. Ito. 2003. Importance of Active Oxygen Scavenging System in the Recovery of Rice Seedlings after Sumbergence. Plant Science Journal., 165:85-93.
FAO. 2005. 20 Hal untuk Diketahui tentang Dampak Air Laut pada Lahan di Provinsi NAD. http://www.fao.org
Gohagu, Y., N.S. Ai and P. Siahaan. 2016. Konsentrasi klorofil pada beberapa varietas tanaman Puring (Codiaeum varigatum L.). Jurnal Mipa Unsrat Online., 5:76-80.
Guo, R., W.P. Hao., D.Z. Gong., X.L. Zhong and F.X. Gu. 2012. Effect of water stress on germination and growth of linseed seedling (Linum usitatissimum L.) photosynthetic efficiency and accumulation of metabolites. Journal of Agricultural Science., 4:253-265.
Gupta, B. and B. Huang. 2014. Mechanism of Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Characterization. International Journal of Genomics., 2014: 1-18.
Ikhwani., E. Suhartatik and A.K. Makarim. 2010. Pengaruh Waktu, Lama, dan Kekeruhan Air Rendaman terhadap Pertumbuhan dan Hasil Padi Sawah IR64-sub1. Penelitian Pertanian Tanaman Pangan., 29:63-71.
Kawano, N., O. Ito and J. Sakagami. 2008. Relationship between shoot elongation and dry weight during submergence in Oryza sativa L. and O. glaberrima Steud. Rice cultivars. Plant Production Science., 11:316-323.
Kementerian Pertanian. 2016. Data Kementan Selaras dengan Data BPS. http://www.pertanian.go.id/ap_posts/detil/1181/2017/09/28/09/30/05/Data%20Kementan%20Selaras%20Dengan%20Data%20BPS
Kementerian Pertanian. 2017. Produksi, Luas Panen, dan Produktivitas Padi di Indonesia, 2013-2017. Jakarta: Kementerian Pertanian.
Kurniasih, B., H. Greenway and T.D. Colmer. 2017. Energetics of acclimation to NaCl by submerged, anoxic rice seedlings. Annals of Botany., 119:129-142.
Kurniawati, S., N. Khumaida., S.W. Ardie., N.S. Hartati and E. Sudarmonowati. 2014. Pola akumulasi prolin dan poliamin beberapa aksesi tanaman terung pada cekaman kekeringan. J. Agron Indonesia., 42:136-141.
Lakitan, B. 1993. Dasar-dasar fisiologi tumbuhan. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada.
Mareja, H.E. 2015. Tanah dan Iklim untuk Pertanaman Padi. https: //cybex.pertanian.go.id/materilokakita/detail/12163/tanah-dan-iklim-untuk-pertanaman-padi/
Mass, E.V. and G. J. Hoffman. 1997. Crop salt tolerance. Current assessment. ASCE Journal of Irrigation Drainage Division., 103:113-134.
Muflikhah, N. 2018. Pertumbuhan dan hasil padi (Oryza sativa L.) Situ bagendit di ledokan dan guludan dengan pengairan salin di lahan sawah Dusun Baros, Bantul, Yogyakarta. Tesis. Program pascasarjana, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.
Muis, A., D. Indradewa and J. Widada. 2013. Pengaruh inokulasi mikoriza arbuskula terhadap pertumbuhan dan hasil kedelai (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) pada berbagai interval penyiraman. Vegetalika., 2:7-20.
Munns, R. and M. Tester. 2008. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol., 59: 651-681.
Peni, D.K., Solichatun and E. Anggarwulan. 2004. Pertumbuhan, Kadar Klorofil-Karotenoid, Saponin, Aktivitas Nitrat Reduktase Anting-anting (Acalypha indica L.) pada Konsentrasi Asam Giberelat (GA3) yang Berbeda. Biofarmasi., 2:1-8.
Rachmawati, D. and E. Retnaningrum. 2013. Pengaruh Tinggi dan Lamanya Penggenangan terhadap Pertumbuhan Padi Kultivar Sintanur dan Dinamika Populasi Rhizobakteria Pemfiksasi Nitrogen non Simbiosis. Bionaturra - Jurnal Ilmu-ilmu Hayati dan Fisik., 15:117-125.
Rad, H.E., F. Aref., M. Khaledian., M. Razaei., E. Amin and O.Y. Falakdehy. 2011. The Effects of Salinity at Different Growth Stage on Rice Yield. ICID 21th International Congress on Irrigarion and Drainage (2011).
Radanielson, A.M., O. Angeles., T. Li., A.M. Ismail and D.S. Gaydon. 2017. Describing the physiological responses of different rice genotypes to salt stress using sigmoid and piecewise linear functions. Field Crop Research., 2017:1-11.
Rivaldi. 2015. Pertumbuhan dan Hasil Padi (Oryza sativa L.) Salibu Varietas Hibrida pada Tinggi dan Waktu Penggenangan. Artikel Ilmiah. Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Tamansiswa. Padang.
Rusd, A.M.I. 2011. Pengujian Toleransi Padi (Oryza sativa L.) terhadap Salinitas pada Fase Perkecambahan. Skripsi. Institut Pertanian Bogor, Bogor.
Sakagami, J., Y. Joho and C. Sone. 2013. Complete submergence escape with shoot elongation ability by underwater photosynthesis in Africa rice, Oryza glaberrima Steud. Field Crops Research., 152:17-26.
Sarkar, R.K., J.N. Reddy., S.G. Sharma and A.M. Ismail. 2006. Physiological Basis of Submergence Tolerance in Rice and Implication for Crop Improvement. Current Science Journal., 91:899-906.
Sasmita, R.K.D. 2006. Dampak pengelolaan fisik tanah terhadap produksi jagung (Zea mays L.) dan efisiensi pemupukan nitrogen dalam sistem pertanian surjan di vertisol. Tesis. Sekolah Pascasarjana, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.
Sudaryono. 2017. Teknologi Produksi Ubikayu di Lahan Pasang Surut Kalimantan Selatan. Makalah. Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pertanian, Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanaman Pangan, Balai Penelitian Tanaman Aneka Kacang dan Umbi, Malang.
Susilawati, A. and D. Nursyamsi. 2014. Sistem surjan: kearifan lokal petani lahan pasang surut dalam mengantisipasi perubahan iklim. Jurnal sumberdaya lahan., 8:31-42.
Sutaryo, B. 2012. Ekspresi Daya Hasil dan Beberapa Karakter Agronomi Enam Padi Hibrida Indica di Lahan Sawah Berpengairan Teknis. Ilmu Pertanian., 15:19-29.
Syamsuddin, D. Indradewa., B.H. Sunarminto and P. Yudono. 2011. Pertumbuhan dan Hasil Dua Kuultivar Padi dan Berbagai Jarak Tanam pada Sistem Pengairan Genangan dalam Parit. J. Agroland., 18:155-161.
Tubur, H.W., M.A.Chozin., E. Santosa and A. Junaedi. 2012. Respon Agronomi Varietas Padi terhadap Periode Kekeringan pada Sistem Sawah. J. Agron Indonesia., 40:167-173.
Yoshiva, S. and L. Castaneda. 1969. Partial replacement of potassium by sodium in the rice plant under weakly saline conditions. Soil science and plant nutrition., 15:183-186.
Zeng, L. and M.C. Shannon. 2000. Effects of Salinity on Grain Yield and Yield Components of Rice at Different Seeding Densities. Journal Agron., 92:418-423.
Zeng, L. 2005. Exploration of Relationships Between Physiological Parameters and Growth Performance of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings under Salinity Stress using Multivariate Analysis. Plant and Soil., 268:51-59.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
Ilmu Pertanian (Agricultural Science) ISSN 0126-4214 (print), ISSN 2527-7162 (online) is published by Faculty of Agriculture Universitas Gadjah Mada collaboration with Perhimpunan Sarjana Pertanian Indonesia (PISPI) and licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.













