The role of iron oxidizing bacteria to the quality of leachate on acid sulphate soil
Khairatun Napisah(1), Azwar Maas(2), Sri Nuryani Hidayah Utami(3*), Wahida Annisa Yusuf(4)
(1) Assessment Institute for Agricultural Technology of South Kalimantan
(2) Department of Soil Science, Faculty Of Agriculture, Universitas Gadjah Mada
(3) Department of Soil Science, Faculty Of Agriculture, Universitas Gadjah Mada
(4) Indonesian Swampland Agricultural Research Institute (ISARI) Banjarbaru
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
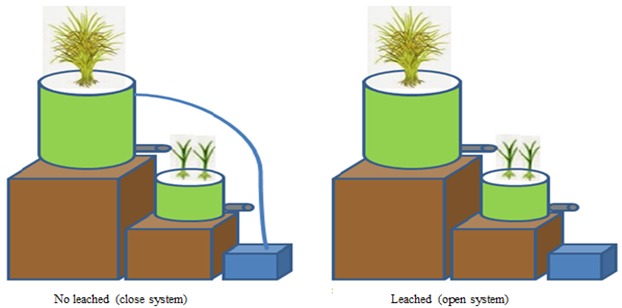
The problem encountered in acid sulphate soil is the presence of pyrite (FeS2) which causes soil to have highly acid reaction when the pyrite is oxidized. The decline in quality not only occurs on the soil but also on the quality of the surrounding waters. One way to improve the quality of the leachate is by draining it through biofilter plants in the form of purun tikus (Eleocharis dulcis) and bulu babi (Eleocharis retroflaxa) which can absorb or neutralize these elements. The purpose of this research was to know the inoculant influence of iron oxidizing bacteria to leachate quality in acid sulphate soil. The research was conducted on a pot scale in greenhouse. The research was in randomized block design (RBD) of 3-factors with 3 replications. The first factor was inoculants, the second factor was water management, and the third one was phytoremediation material (Eleocharis dulcis and Eleocharis retroflaxa). The results showed that the plant height in the inoculant treatment+wood charcoal was in the range of 89.33−95.33 cm, while that in the inoculant treatment+husk charcoal was in the range of 89.50−93.00 cm. Meanwhile, the yield of rice with bacteria oxidizing iron inoculant+wood charcoal was higher, which was at 6.77 ton.ha-1 than inoculant treatment of oxidizing iron+husk charcoal which was only 5.95 ton.ha-1.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Aksani, D. 2016. Peningkatan pH Tanah Pada Budidaya Padi Lahan Pasang Surut Melalui Aplikasi Pupuk Cair dari Neptunia Prostrata. Dalam Prosiding Seminar Nasional Lahan Suboptimal. Palembang. Hal 584-591.
Alia, O., M. Laila, and A. Antonius. 2013. Antimicrobial Effect of Melittin Isolated From Syrian Oneybee (Apis Mellifera) Venom and Its Wound Healing Potential. Int J. Pharm Sci Rev Res., 21: 318-324.
Annisa, W. 2014. Peran Bahan Organik Dan Tata Air Mikro Terhadap Kelarutan Besi, Emisi CH4, Emisi CO2 dan Produktivitas Padi di Lahan Sulfat Masam. Universitas Gadjah Mada,Yogyakarta, 66-67. (Disertasi)
Asikin, A. dan M. Thamrin. 2012. Manfaat Purun Tikus (Eleocharis dulcis) Pada Ekosistem Rawa. Jurnal Litbang Pertanian, 31: 35 – 42.
Bacelor-Nicolau, P., and D. B. Johnson. 1999. Lounching of Piryte by Acidophillie Iron Oxidating-Bacteria. J Apple/Env. Microbial, 65(2): 585-590.
Balitbangtan. 2013. Lahan Rawa. Edisi ke 2, Jakarta: IAARD Press, Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pertanian, Kementerian Pertanian.
Balittanah. 2012. Analisis Kimia Tanah, Tanaman, Air, dan Pupuk. Edisi ke 2, Bogor: Balai Penelitian Tanah.
Becker, M. and F. Ash. 2005. Iron Toxicity in Rice Condition and Management Concept. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 168 : 558-573.
Haynes, R.J. and Mokolobate, M.S. 2001. Amelioration of Al Toxicity and P Deficiency in Acid Soil by Additions of Organic Residues: A Critical Review of The Phenomenon And The Mechanisms Involved. Nutrient Cycling In Argoecosystems, 59: 47-63.
Hazra, F dan E. Widyati, 2007. Isolasi, Seleksi Bahan Pembawa dan Formulasi Inokulam Thiobacillus spp. Jurnal Tanah dan Lingkungan, 9:71-76.
Lu, H.L., C.R. Ku., and Y.H. Chang. 2015. Water Quality Improvement With Artificial Floating Islands. Journal Ecological Engineering, 75: 371-375.
Jumberi, A., M. Syarwani, dan Koesrini. 2004. Komponen Teknologi Pengelolaan Lahan dan Tanaman Untuk Meningkatkan Produktifitas dan Efisiesi Produksi Di Lahan Sulfat Masam. p. 9-14. In: T. Alihamsyah dan N. Izzuddin. Laporan Tahunan 2003. Banjarbaru : Balai Penelitian Pertanian Lahan Rawa.
Maftuah, E., dan A. Susilawati. 2018. Bioleaching Untuk Meningkatkan Produktivitas Lahan Sulfat Masam Aktual Untuk Tanaman Padi. Jurnal Ilmu-Ilmu Hayati, 17: 253-264.
Mariana, Z.T., F. Razie, M. Septiana. 2012. Populasi bakteri Pengoksidasi Besi dan Sulfur Akibat Penggenangan dan Pengeringan Pada Tanah Sulfat Masam di Kalimantan Selatan. Jurnal Agroscientiec, 19: 22-27.
Marschner, H. 1986. Mineral Nutrion of Higher Plants. 2nd ed., London:Academic Press Inc., London.
Masganti. 2011. Perbedaan Daya Serap Hara Beberapa Varietas Unggul Padi Pada Tipe Lahan Berbeda di Lahan Pasang Surut. Jurnal Penelitian Pertanian Tanaman Pangan, 30:23-29.
Napisah, K., dan W. Annisa. 2019. Peran Purun Tikus (Eleocharis dulcis) sebagai Penyerap dan Penetral Fe di Lahan Rawa Pasang Surut. Jurnal Sumberdaya Lahan, 13: 53-59.
Notohadiprawiro, T. 2000. Tanah dan Lingkungan. Edisi ke 2, Yogyakarta: Gadjah Mada University Press.
Nurseha dan Djajakirana G. 2004. Isolasi dan Uji Aktivitas Bakteri Asidofilik Pengoksidasi Besi Dan Sulfur Dari Ekosistem Air Hitam di Kalimantan Tengah. Jurnal Tanah dan Lingkungan, 6: 51-56.
Ponnamperuma. 1977. Behavior of Minor Elements in Paddy Soils. 8th ed., Manila: International Research Institute, Philippines.
Pusparani, S. 2018. Characterization of Soil Physic And Chemistry Properties of Mineral Acidic Sulphate Soil on Tidal Land. Jurnal Hexagro, 2: 1-4.
Satawathananont, W.H. Patrick and P.A. Moore. 1991. Effect of Controlled Redox Conditions on Metal Solubility In Acid Sulphate Soil. J. Plant and Soil, 133: 281-290.
Su, J.Q., Y. Xia, H.Y. Yao, Y.Y. Li, X.L. An; B.K. Singh, T. Zhang, and Y.G. Zhu. 2017. Metagenomic Assembly Unravel Microbial Response to Redox Fluctuation In Acid Sulfate Soil. Journal Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 105: 244-252.
Susilawati, A. and A. Fahmi., 2013. Dinamika Besi pada Tanah Sulfat Masam Yang Ditanami Padi. Jurnal Sumberdaya Lahan, 7: 67-75.
Sulistiyani, D.P., Napolean, A.G. Putra. 2014. Penilaian Kualitas Tanah Pada Lahan Rawa Pasang Surut Untuk Tanaman Jagung (Zea mays L) Di Desa Banyu Urip Kecamatan Tanjung Lago Kabupaten Banyuasin. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Lahan Suboptimal, 812-820. (Abstr.)
Yuliana, E.D. 2012. Jenis Mineral Liat dan Perubahan Sifat Kimia Tanah Akibat Proses Reduksi dan Oksidasi Pada Lingkungan Tanah Sulfat Masam. Jurnal Bumi Lestari, 12:327-337.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Ilmu Pertanian (Agricultural Science) ISSN 0126-4214 (print), ISSN 2527-7162 (online) is published by Faculty of Agriculture Universitas Gadjah Mada collaboration with Perhimpunan Sarjana Pertanian Indonesia (PISPI) and licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.














