PEMBUATAN MEMBRAN SERAT BERONGGA POLIETERSULFON/2-(METAKRILOILOSI)ETIL POSPORIL KLORIN DAN APLIKASINYA UNTUK PENGOLAHAN AIR SUMUR TERCEMAR LIMBAH TSUNAMI DI BANDA ACEH (Preparation Hollow Fiber Membrane of Polyethersulfone/2-(Methacryloyloxy)
Sri Aprilia(1*), Nasrul Arahman(2)
(1) Jurusan Teknik Kimia, Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Syiah Kuala Jalan Syech Abdurrauf No 7, Darussalam, Banda Aceh 23111.
(2) Jurusan Teknik Kimia, Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Syiah Kuala Jalan Syech Abdurrauf No 7, Darussalam, Banda Aceh 23111.
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
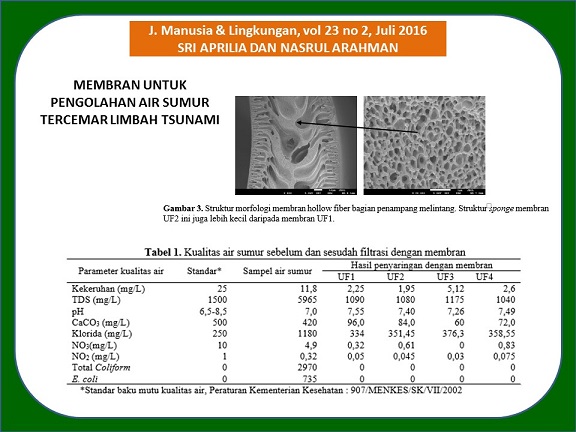
Banyak kasus air sumur masyarakat di wilayah yang terkena imbas tsunami di Banda Aceh mengandung zat padat terlarut (Total Dissolved Solid, TDS) dan klorida melebihi standar baku mutu untuk pertimbangan kesehatan. Diperlukan perlakuan khusus untuk menghilangkan zat padat terlarut dan klorida dari air tersebut. Teknologi membran telah diperkenalkan secara luas sebagai teknik yang menjanjikan untuk produksi air bersih dengan kualitas tinggi. Pada penelitian ini, teknik separasi dengan lapisan membran digunakan untuk memisahkan kandungan zat padat terlarut dan klorida dari sampel air sumur masyarakat Banda Aceh yang terkena tsunami. Membran serat berongga dibuat dengan melarutkan polietersulfon and 2-(metakriloiloksi)etil posporil klorin ke dalam pelarut N-metil-2-pirolidon. Studi ini mempelajari pengaruh konsentrasi membran modifying agent terhadap struktur morfologi membran yang dihasilkan. Kemudian kinerja membran terhadap filtrasi dilakukan dengan menggunakan air deionisasi. Lebih lanjut, kinerja membran dilakukan untuk mengurangi kadar kekeruhan, TDS, CaCO3, Cl, NO3, NO2, total coliform, dan bakteri Escherichia coli dari sampel air sumur. Hasil ekperimen menunjukkan bahwa semua parameter yang diuji dapat dikurangi sampai nilainya berada di bawah standar baku mutu air bersih.
ABSTRACT
In many cases well water on tsunami affected area of Banda Aceh contains the Total Dissolved Solid (TDS) and chloride in high concentration over the drinking water level for general good health consideration. A special treatments are needed to remove the TDS and chloride in water. Membrane technology have been widely introduced as an emerging technique to produce high quality of clean water. In this work, membrane separations are proposed to remove TDS and chloride from well water of community in tsunami affected area of Banda Aceh. Membrane hollow fiber was prepared by dissolving of polyethersulfone and 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl phosphoryl chlorine in N-methyl-2-pirrolydone. The effect of membrane modifying agent concentration studied on the morphology of resulted membrane. The fabricated membrane was used to observe the filtration performance of deionized water by using single module of hollow fiber membrane. In addition, the membrane was used to remove turbidity, TDS, CaCO3, Cl, NO3, NO2, total coliform, and Escherichia Coli bacteria from sample of well water. The experimental result showed that all parameter can be reduced and those concentration was under the quality standard of drinking water.
Keywords
Full Text:
ARTIKEL LENGKAP (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)References
Arahman, N., Arifin, B., Mulyati, S., Ohmukai, Y., dan Matsuyama, H., 2011. Improved Fouling Reduction of PES Hollow Fiber Membranes by Incorporation with Non-ionic Surfactant. Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment, 15:212-216,
Baker, R.W. 2004. Membrane Technology and Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Chowdhury, S., Champagne, P. dan McLellan, J., 2010. Investigating Effects of Bromide Ions on Trihalomethanes and Developing Model for Predicting Bromodichloromethane in Drinking Water. Water Research, 44(7):2349-2359.
Chu, W., Gao, N., Yin, D., dan Krasner, A.W., 2013. Formation and Speciation of Nine Haloacetamides, an Emerging Class of Nitrogenous DBPs, During Chlorination or Chloramination. Journal of Hazardous Material, 260:806-812.
Culin, J., dan Mustac, B., 2015. Environmental Risks Associated with Ballast Water Management Systems that Create Disinfection By-Products (DBPs). Ocean & Coastal Management, 105:100-105.
Ilyas, M, Arahman, N, dan Tarmizi, S.A., 2006. Kualitas Air Sumur Perumahan Masyarakat Kota Banda Aceh Pasca Bencana Alam Gempa Bumi dan Tsunami 26 Desember 2004. Laporan hasil penelitian. Kerja sama dengan Japan NGO Network on Indonesia (JANNI).
Kumari, M., Gupta, S.K., Mishra, B.K., 2015. Multi-exposure Cancer and Non-cancer Risk Assessment of Trihalomethanes in Drinking Water Supplies – A Case Study of Eastern region of India. Ecotoxicology and Environmetal Safety, 113:433-438.
Kumar, R., Isloor, A.M., Ismail, A.F., dan Matsura, T, 2013. Performance Improvement of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membrane Using N-succinyl Chitosan as Additive. Desalination, 318:1-8
Lalia, B.S., Kochkodan, V., Hashaikeh, R., dan Hilal, N., 2013. A Review on Membrane Fabrication: Structure, Properties and Performance Relationship, Desalination, 326:77-95.
Martín, A., Arsuaga, J.M., Roldán, N., Abajo, J., Martínez, A., dan Sotto, A., 2015. Enhanced Ultrafiltration PES Membranes Doped with Mesostructured Functionalized Silica Particles. Desalination, 357:16-25.
Matsumaru, R., Nagami, K., dan Takeya, K., 2012. Reconstruction of the Aceh Region Following the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami Disaster: A Transportation Perspective. IATSS Research, 36:11–19.
Miswadi, S.S., 2009. Kajian Spasial Kualitas Air Tanah Bebas Berdasarkan Kedalaman Muka Air Tanah: Studi Kasus di Daratan Aluvial Das Pemali Kabupaten Brebes. Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan, 16(2):103-114.
Mohammad, A.W., Teow, Y.H., Ang, W.L., Chung, Y.T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L., Hilal, N., 2015. Nanofiltration Membranes Review: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Desalination, 356:226-254.
Pearce, G, 2007. Introduction to Membranes: Filtration for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Filtration+Separation, 44:24-27.
Su, Y-N., Lin, W-S., Hou, C-H, dan Den, W., 2015. Performance of Integrated Membrane Fltration and Electrodialysis Processes for Copper Recovery from Water Polishing Wastewater. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 4:149-158.
Sun, Y-X., Wu, Q-Y., Hu, H-Y., dan Tian, J., 2009. Effect of Ammonia on the Formation of THMs and HAAs in Secondary Effluent Chlorination. Chemosphere 76:631–637.
Tokmak, B., Capar, G., Filiz B. Dilek, dan Ulku Yetis, 2004. Trihalomethanes and Associated Potential Cancer Risks in the Water Supply in Ankara, Turkey. Environmental Research 96:345–352.
Widyastuti, M., Sudarmadji, Sutikno, dan Hendrayana, H., 2012. Kerentanan Ait Tanah terhadap Pencemaran Daerah Imbuhan Ponor di Karst Gunung Sewu (Studi di Daerah Aliran Bawah Tanah Bribin). Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan, 19(2):128-142
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







