EFFECTS OF ECONOMIC BEHAVIOUR AND PEIPLE MIGRANTION ON THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MALARIA : A MODEL BASED STUDY
Sajal Bhattacharya(1*), Debabrata Datta(2)
(1) Department of Zoology and Post Graduate Department of Environmental Science, Asutosh College (University of Calcutta), Kolkata – 700026, India
(2) Department of Economic, Asutosh College (University of Calcutta), Kolkata-700026, India
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
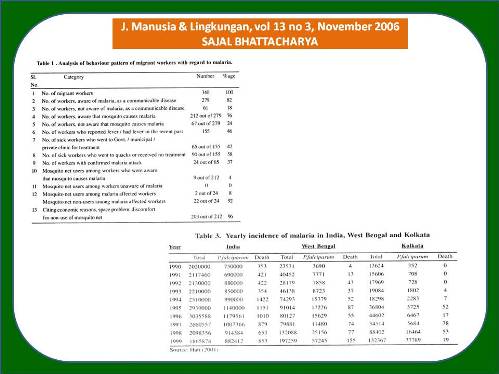
The objective of the paper is to study the socio economic behaviour of migrant labourers in the context of the control of the diseases like malaria. The paper, therefore, makes a model and survey based study in the city of Kolkata, India to drive home the point that low income of people particularly of the migrant workers can be a major hurdle in the malaria control programme. The paper first looks at the economic behaviour pattern theoretically from neo-classical optimization exercise and the tries to test the theoetical result empirically from primary survey. The theoritical model gives the result that low income people is likely to take less rest and discontinue medical tratment. Since migrant workers of less developed counties are usually low-income people, pur model suggests that migrant workers will have incomplete treatment and their migration even before complete recovery may contribute to spread of the disease. We hage empirically tested the model econometrically by a logit model, and derived the result that migrat workers do take less rest and discontinue treatment becouse of economic compulsion. Thus the data support the result of the theoretical model and refeals a behafiour pattern, conducive to spread of malaria infection. The paper drives some policy prescriptions on the basis of these studies like infurance support, health survillance of migrant population as a part of integrated malaria control programme.
Full Text:
Artikel lengkap (PDF)Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







