KERENTANAN PENYUSUPAN AIR LAUT DI PESISIR UTARA PULAU TERNATE (Vulnerability of Sea Water Intrusion in Northern Coastal of Ternate Island)
Rahim Achmad(1*), Muhammad Pramono Hadi(2), Setyawan Purnama(3)
(1) Program Studi Geografi, Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Khairun, Jl. Bandara Babullah, Ternate 97714
(2) Fakultas Geografi, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Sekip Utara Yogyakarta 55281
(3) Fakultas Geografi, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Sekip Utara Yogyakarta 55281
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
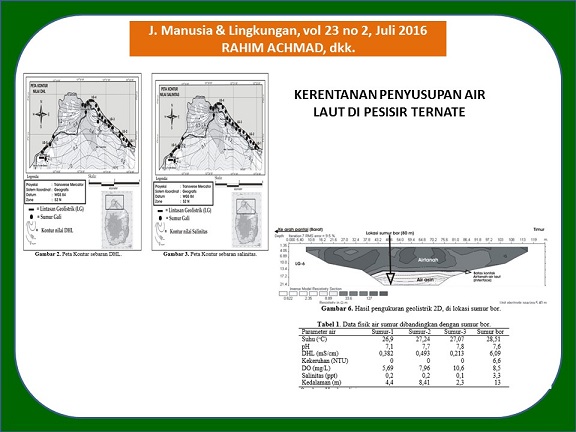
Penelitian ini dilakukan di wilayah pesisir bagian utara Pulau Ternate, dengan tujuan mengetahui kedalaman batas kontak airtanah dengan air laut dan menganalisis akuifer serta cara pengambilan airtanah sehingga tidak terjadi penyusupan air laut ke dalam tubuh airtanah. Sampel air sumur diukur untuk mengetahui kadar salinitas dan daya hantar listrik (DHL). Kedalaman batas kontak airtanah dengan air laut dukur dengan menggunakan metode geolistrik. Hasil pengukuran DHL dan salinitas airtanah di wilayah pesisir utara menunjukkan, terdapat penyusupan air laut di Desa Tobolo dan Sulamadaha, dengan rentang nilai masing-masing antara 0,5-3,3 mS/cm dan 0,2-1,7 ppt. Hasil pengukuran geolistrik menunjukkan batas kontak airtanah dengan air laut rata-rata antara 12-15 m dari permukaan. Nilai resistivitas air laut berkisar antara 0,01-20 Ωm. Hasil penelitian ini memberikan peringatan untuk tidak melakukan pengeboran sumur di wilayah pesisir. Sebagai contoh kasus, pengeboran sumur hingga 80 m dengan jarak sekitar 250 m dari garis pantai di Desa Takome, di mana batas kontak airtanah dengan air laut pada kedalaman 15 m. Pengukuran nilai DHL dan salinatas air dari sumur ini menunjukkan masing-masing 6,1 mS/cm dan 3,3 ppt. Nilai ini menunjukkan kedalaman sumur bor telah melewati zona pencampuran antara airtanah dengan air laut (interface).
ABSTRACT
This research was conducted in the coastal areas of northern part of Ternate island, in order to know the depth of interface and to analyze the aquifers and to avoid seawater intrusion caused of groundwater extraction. Well water samples were measured to determine levels of salinity and DHL. The depth of interface was measured using geoelectric method. The results of electrical conductivity (EC ) and salinity of groundwater measurement in the northern coastal area showed that, there is infiltration of sea water in Tobolo and Sulamadaha. The EC and salinity values ranging between 0.5-3.3 mS/cm and 0.2-1.7 ppt respectively. The geoelectric measurement results showed that the depth of interface ranging between 12-15 m from the surface. The resistivity of saline water values ranging between 0.01-20 Ωm. This research provides a warning for not drilling well in coastal areas . For example case, a drilled well with a depth 80 m, located about 250 m from the shoreline in village Takome, where the depth of the interface is 15 m. The value of EC and saline water were measured from this drilled well showed 6.1 mS/cm and 3.3 ppt respectively. This value indicates the depth of the drilled well has exceeded the interface zone.
Keywords
Full Text:
ARTIKEL LENGKAP (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)References
Abdullah, M.H., Raveena, S.M., dan Aris, A.Z., 2010. A Numerical Modelling of Seawater Intrusion into an Oceanic Island Aquifer. Journal Sains Malaysiana, 39(4):525-532.
Achmad, R., 2014. Groundwater Flow and Subsurface Structures of Small Volcanic Island Based on Geophysical Measurements. Celebes International Conference on Earth Science, Kendari, 10-11 November 2014.
Brahim, F., Khanfir, H., dan Bouri, S., 2012. Groundwater Vulnerability and Risk Mapping of the Northern Sfax Aquifer, Tunisia. Arab Journal Science Enginering, 37(1):1405–1421.
Bronto, S., Hadisantoso R.D., dan Lockwood, J.P., 1982. Peta Geologi Gunungapi Gamalama, Ternate Maluku Utara. Direktorat Vulkanologi, Bandung.
Delinom R,M., dan Lubis R.F., 2007. Airtanah di Pesisir dan Pulau Kecil. Prosiding LIPI, LIPI Press, Jakarta, hal. 1-26.
Falkland, A.C., 2014. Climate Change 2014; Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Cambridge University Press, London, p.336.
Fetter, C.W, 2004. Applied Hydrogeology. 4th edition, Mac Millan Publishing, New York.
Gaaloul, N., Pliakas, F., Kallioras, A,. Schuth C., dan Marinos, P., 2012. Simulation of Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers. The Open Hydrology Journal, 6:31-44.
Guha H., dan Panday S., 2012. Impact of Sea Level Rise on Groundwater Salinity in a Coastal Community of South Florida. Journal of The American Water Resources Association, 48(3):510-929.
Hehanusa, P.E., dan Bakti, H., 2005. Sumber Daya Air Pulau Kecil. LIPI Press, Bandung.
Latief., 2005. Kajian Airtanah Pulau Ternate, Tesis Fakultas Teknik Pertambangan ITB, Bandung.
Loke, M.H., 2004. Rapid 2-D Resistivity & IP Inversion Using The Least-Squares Method, On Land, Underwater and Cross-borehole Surveys, Penang.
Miswadi, S.S., 2010. Penurunan Tingkat Intrusi Air Laut Berdasarkan Chloride Bicarbonate Ratio Menggunakan Lubang Resapan Biopori. Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan, 17(3):150-161
Numberi F., 2009. Perubahan Iklim, Implikasinya Terhadap Kehidupan di Laut, Pesisir dan Pulau Kecil. Penerbit Fortuna, Jakarta, pp. 56-62.
Pontoh, E.S., 2007. Kajian Potensi Airtanah Pulau Ternate Propinsi Maluku Utara. Tesis Fakultas Teknik Geologi, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.
Purnomo, B.J., 2009. Laporan Evaluasi Potensi Cekungan Airtanah (CAT) Pulau Ternate. Badan Geologi Lingkungan, Bandung, pp. 8-10.
Santosa, L.W., 2010. Pengaruh Genensis Bentuk Lahan Terhadap Hidrostratigrafi Akuifer dan Hidrogeokimia dalam Evolusi Airtanah Bebas. Disertasi, Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.
Sherif, M., Sefelnasr, A., dan Javadi, A., 2012. Incorporating the Concept of Equivalent Freshwater Head in Successive Horizontal Simulations of Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. Journal of Hydrology, 464-465:186-198.
Todd, D.K., dan Mays, L.W., 2005. Groundwater Hydrology. 3rd Ed., John Willey and Sons, New York.
Werner. A. D., dan Simmons, C.T., 2009. Impact of Sea-Level Rise on Sea Water Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers. Journal of Ground Water, 47(2):197-204.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







