PENENTUAN KRITERIA NUTRIEN UNTUK PENILAIAN STATUS TROFIK PERAIRAN WADUK MRICA BANJARNEGARA, INDONESIA (Determination of nutrient criteria for assessing trophic status of Mrica Reservoir Banjarnegara, Indonesia)
Agatha Sih Piranti(1*), Sudarmadji Sudarmadji(2), Agus Maryono(3), Suwarno Hadisusanto(4)
(1) Fakultas Biologi UNSOED Purwokerto
(2) Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta
(3) Fakultas Teknik Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta
(4) Fakultas Biologi Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
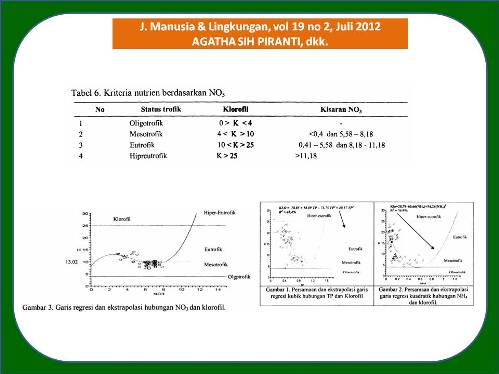
Saat ini kriteria nutrien yang sering digunakan untuk penilaian status trofik suatu badan air di Indonesia adalah berdasarkan OEeD (1982), dan Mason (1991) yang merupakan hasil kajian status trofik danau dan waduk di wilayah empat musim (temperate). Kriteria tersebut bila digunakan untuk waduk di Indonesia sering tidak mencerminkan kondisi yang sebenamya karena ada perbedaan mekanisme terjadinya eutrofikasi di wilayah tropis dan temperate (Huszar et al., 2006). Tujuan peneiitian ini adalah mengkaji hubungan antara konsentrasi nutrien dengan biomassa algae sebagai dasar untuk menentukan kriteria nutrien yang tepat sebagai upaya penentuan kriteria trofik waduk di Indonesia. Metode peneiitian menggunakan survei dengan mengambil sampel air sebulan sekali selama 1 (satu) tahun mulai Maret 2009 -Februari 2010 di 11 (sebelas) lokasi di perairan Waduk Mrica Banjamegara. Variabel penelitian adalah Total Nitrogen (TN), Total Fosfat (TP), nitrat (NO]), ortofosfat (P04), ammonia ~), TN/TP, dan klorofil. Kesimpulan adalah kriteria TP untuk mencapai fase eutrofik pad a musim penghujan lebih tinggi (TP ~ 1,55 mg/I) dibandingkan musim kemarau (TP ~ 1,33). Pada musim penghujan maupun kemarau total nitrogen (TN) bukan merupakan nutrien pembatas. Nutrien (N dan P) yang tinggi (bahkan mencapai 10 kali iipat lebih tinggi dibandingkan kriteria nutrien dari wilayah temperate) tidak menirnbulkan blooming. Terjadinya blooming algae di Waduk Mrica disebabkan adanya operasional waduk dan didukung oieh kondisi iklim (cahaya dan suhu) yang tidak menjadi faktor pembatas pertumbuhan algae. Oleh karena itu, kriteria nutrien untuk danau di wilayah sub tropis tidak cocok bila digunakan untuk penilaian status trofik untuk waduk di Indonesia.
ABSTRACT
A nutrient criteria currently used for the assessment of trophic status of water bodies in Indonesia are based on OECD (1982), and Mason (1991) resulted from lakes and reservoirs’ trophic status study of temperate region. These criteria when used for reservoirs in Indonesia often did not reflect the actual conditions because there are differences in the mechanisms of eutrophication in tropical and temperate regions (Huszar et al., 2006). The purposes of this research were to study the relationship between nutrient and algae biomass in order to determine nutrient criteria properly for assessing the trophic levels of reservoir waters in Indonesia.This research was conducted by surveys by taking samples of water once a month for 1 (one) year from March 2009 to February 2010 in eleven locations of Mrica reservoir. Research variables were total nitrogen (TN), total posfat (TP), nitrate (NO3), orthophosphate (PO4), ammonium (NH4), TN/TP, NO3/PO4 and chlorophyll. It can be concluded that The TP criteria of eutrophic phase during rainy season (TP > 1,55 mg/l) was higher than of dry season (TP > 1,33). During both rainy or dry season TN was not a limiting nutrient of algae growth even it was always needed. The very high nutrient (even ten-fold higher than in temperate region) not resulted in algae bloom. This might due to the process of electricity generating and flushing also the climate regimes (light and temperature) were not become a limiting factor for algae growth. Therefore, the nutrient criteria based on temperate region was not work properly if used for assessment of trophic status in Indonesia.
Keywords
Full Text:
ARTIKEL LENGKAP (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







